How to fix "Duplicate without User-Selected Canonical" in Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) helps webmasters identify indexing issues, including “Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical.” This means that Google has found duplicate content on your site without a designated canonical URL, which can dilute SEO rankings and waste crawl budget if left unresolved.
This guide will help you understand, troubleshoot, and effectively prevent “duplication without user-selected canonical” issues.
What Does “Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical” Mean?
This message appears when Google discovers multiple versions of a page without a unique canonical URL. Canonical tags help ensure consistent indexing by guiding search engines to prioritize one version of the content.
Common examples of duplicates (read more details about the most common causes below):
- URLs with parameters (e.g.,
?utm_source=google). - HTTP and HTTPS versions.
- Pages accessible via
wwwandnon-www.
Why Should You Care About Fixing This?
You have 2 main reasons to be concerned about this issue: its impact on SEO and user experience.
SEO Impact:
- Crawl efficiency: When there are duplicate pages, Google’s crawl budget is spent indexing redundant content instead of unique, valuable pages. The result can be a delay in the discovery of important updates or new pages.
- Ranking Cannibalization: When there are multiple URLs competing for the same keywords, it’s more difficult for Google to determine which version to rank, resulting in diluted visibility and lower overall rankings for your site.
- De-indexing risk: Google may index a less relevant duplicate or exclude your preferred version altogether, harming your site’s search visibility.
User Experience:
- Broken Navigation: Duplicate content often creates inconsistent or conflicting navigation paths, confusing users.
- Inaccurate search results: Visitors may end up on outdated or less relevant pages. This can affect their trust and engagement with your site.
Identifying the Scope of the Issue
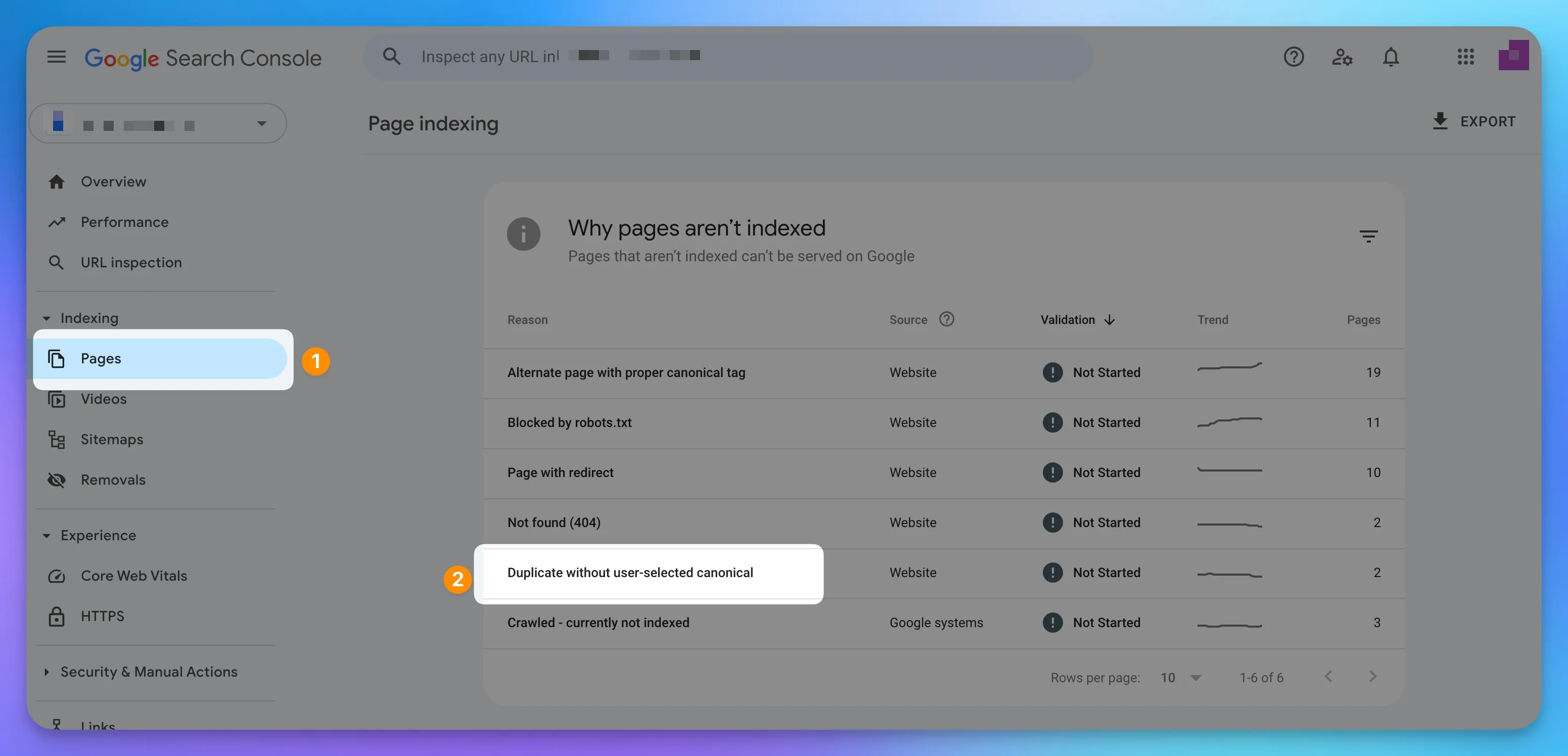
You can easily find all the pages using Google Search console:
- Navigate to the Indexing section and click on Pages section to see all the issues.
- Click on the sub-section named
Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical.
Some free tools that can help:
- Screaming Frog or Sitebulb: Identify duplicate URLs and implement the canonical tag.
- Ahrefs or Telescope: Analyze the backlinks to the duplicate pages.
Common Causes of Duplicate Content Without Canonical Tags
Here are the most common reasons that can cause the problem of “duplicate content without canonical tags”.
- Dynamic URLs: Dynamic URLs often contain session IDs, UTM parameters, or filter options. These can create multiple versions of the same page. For example:
https://example.com/product?id=12345https://example.com/product?id=12345&utm_source=googlehttps://example.com/product?filter=color
- CMS Issues: Many content management systems create duplicate pages by default. Examples include category archives, tag pages, and author archives. For example:
https://example.com/category/widgetshttps://example.com/category/widgets/page/2https://example.com/tag/widgets
- URL Variations: Variations in URLs can cause duplicates, such as:
- HTTP vs. HTTPS:
http://example.com/pagehttps://example.com/page
- Trailing slashes vs. non-trailing slashes:
https://example.com/pagehttps://example.com/page/
- Case Sensitivity:
https://example.com/Pagehttps://example.com/page
- HTTP vs. HTTPS:
- Misconfigured Canonical Tags: Canonical tags that incorrectly point to a duplicate version instead of the preferred one can exacerbate the issue. For example:
- Canonical tag on
https://example.com/page1incorrectly points tohttps://example.com/page2. - Canonical tags conflict between HTTP and HTTPS versions.
- Canonical tag on
- Scraped Content: Content copied by other websites can lead to duplicates appearing on external domains, potentially harming your authority. For example:
- Original:
https://example.com/blog-post - Copied:
https://scraper-site.com/copied-article.
- Original:
How to Resolve “Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical”
Let’s talk about how you can fix these issues.
- Proper use of canonical tags: Canonical tags are essential. They direct search engines to the preferred version of a page. For example, if you have two duplicate URLs, such as
https://example.com/page1andhttps://example.com/page1?ref=source, you can add<link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/page1" /\>to both pages to ensure that search engines prioritizehttps://example.com/page1. Always check canonical tags to make sure they point to the correct, unique URL. - 301 Redirects: Implement 301 redirects to consolidate duplicate pages. For example, if both
http://example.comandhttps://example.comare accessible, redirect the HTTP version to HTTPS. Similarly, redirecthttps://example.com/page/tohttps://example.com/pageif the latter is the preferred version. Avoid 302 redirects, as they are temporary and do not carry full ranking signals. - Fix internal links: Check your site’s internal links to make sure they consistently point to the canonical version of each page. For example, links such as
https://example.com/page?ref=blogshould be updated tohttps://example.com/page. Fixing broken or outdated links ensures a clear path for both users and search engines. - CMS customizations: Most content management systems (CMS) create duplicate pages by default, such as category or archive pages. Use SEO plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math to automatically configure canonical tags for these pages. For example, if your WordPress site generates
https://example.com/category/widgetsandhttps://example.com/widgets, make sure the canonical tag on the category page points to the main page (https://example.com/widgets). In addition, disable any archives that are not necessary for the structure of your site.
Preventing Future Duplicate Issues
Proactive measures and consistent monitoring are required to prevent duplicate content issues. During the development phase, start by establishing clear canonical rules. For example, ensure that dynamic page templates automatically insert canonical tags such as <link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/page" /> for each dynamically generated page.
Education is also critical. Educate your content creators and developers about the importance of canonical tags and the risks of duplicate content. For example, emphasize linking to canonical URLs in internal links. Avoid unnecessary parameterized URLs.
A key role is played by regular monitoring. Use tools such as Google Search Console to keep track of newly flagged duplicate pages, and combine this with site crawlers such as Screaming FrogScreaming Frog to identify and fix duplicate pages before they become a problem. Conduct thorough SEO audits on a monthly or quarterly basis. This will ensure that any new issues are identified and resolved early. Audits check for canonical tag consistency, URL structures, and crawl reports. This ensures a clean and efficient index.
Advanced Troubleshooting and Edge Cases
When tackling advanced issues related to duplicate content, start by reviewing the canonical tag implementation. If canonical tags are being ignored by Google, check for common problems such as conflicting signals between canonical tags, redirects, and noindex tags. For instance, a page with both a canonical tag and a noindex directive may confuse search engines.
For multilingual sites, ensure you use <link rel="alternate" hreflang="x" /> tags in addition to canonical tags. This setup helps Google understand regional and language-specific versions of your site. For example, if you have English (https://example.com/en) and Spanish (https://example.com/es) versions of a page, include the proper hreflang attributes linking them together.
Scraper issues often arise when unauthorized websites copy your content, which can result in duplicate content penalties. Use canonical tags on your original pages to signal ownership. For example, add <link rel="canonical" href="https://example.com/original-content" /> to your content pages. Additionally, consider filing DMCA complaints against scraper sites to remove unauthorized copies from search engine results.
Measuring the Impact of Your Fixes
Start with Google Search Console to evaluate the effectiveness of your fixes. Check the Index Coverage report for updates. In particular, look for previously flagged duplicate URLs to see if they are now indexed correctly. Also confirm that Google recognizes canonical tags and indexes the correct version of each page using the URL Inspection tool.
To ensure that Google’s bots are prioritizing unique, high-quality pages, examine crawl logs using tools such as Screaming Frog or server log analyzers. Look for a decrease in crawl activity for duplicate URLs. This indicates that the fixes are being followed.
Use tools such as Google Analytics and Telescope to monitor your rankings and traffic metrics for key pages. For pages affected by duplicate content issues, check for improvements in search visibility and organic traffic. For example, check to see if the canonical version now ranks higher in search results if https://example.com/page used to compete with https://example.com/page?ref=source.
With the combination of these methods, you can clearly measure how effectively your changes have resolved the issue and improved the performance of your site.
Final Thoughts
Duplication without user-selected canonicals can have a major impact on SEO and user experience. You can ensure efficient crawling, better rankings, and improved site performance by identifying, resolving, and preventing duplicate content.
Proactive management is key - stay ahead by auditing regularly and having a strong canonical strategy.