Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A Content Delivery Network, or CDN, is a geographically distributed network of servers that work together to deliver web content quickly and efficiently to users across the globe. Instead of serving content from a single origin server, CDNs store cached versions of your website’s static content on multiple servers worldwide, known as edge servers or Points of Presence (PoPs).
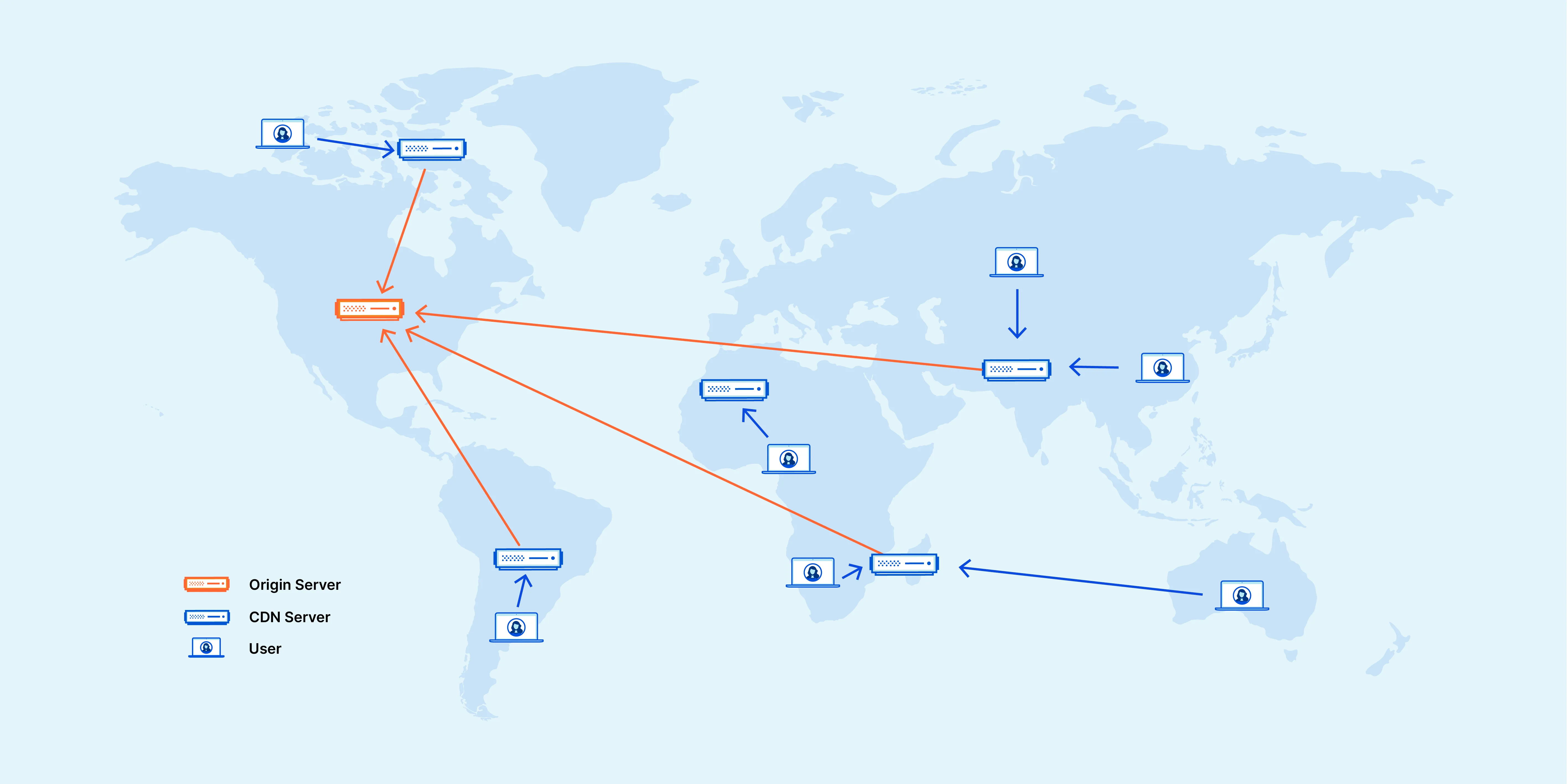
How Does a CDN Work?
- Content Caching: When a user requests content from a website, the CDN redirects the request to the nearest edge server.
- Edge Server Selection: The CDN uses various algorithms to determine the optimal server based on factors like geographic location, server load, and content availability.
- Content Delivery: If the edge server has the requested content cached, it delivers it directly to the user. If not, it retrieves the content from the origin server, caches it, and then serves it to the user.
- Dynamic Content Handling: While CDNs primarily cache static content, many modern CDNs can also accelerate dynamic content delivery through various optimization techniques.
An illustration of how a CDN works from Cloudflare:
Benefits of Using a CDN
1. Improved Website Speed
By serving content from servers closer to the user’s geographic location, CDNs significantly reduce latency and improve load times.
2. Reduced Bandwidth Costs
CDNs offload traffic from your origin server, potentially reducing your hosting costs and bandwidth usage.
3. Enhanced Website Reliability
Distributing content across multiple servers improves redundancy and reduces the risk of website downtime due to server failures or traffic spikes.
4. Improved SEO Performance
Faster load times and improved user experience can positively impact your search engine rankings.
5. Global Reach
CDNs make it easier to serve content to a global audience with consistent performance, regardless of geographic location.
6. DDoS Protection
Many CDNs offer built-in security features, including protection against Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
7. SSL/TLS Offloading
CDNs can handle SSL/TLS encryption, reducing the computational load on your origin server.
Types of Content Suitable for CDN Delivery
- Static assets (images, CSS, JavaScript files)
- Video and audio files
- Downloadable content (PDFs, software updates)
- API responses
- Static HTML pages
Choosing the Right CDN Provider
When selecting a CDN provider, consider the following factors:
- Global Network Coverage: Ensure the provider has a robust network of edge servers in regions where your target audience is located.
- Performance Metrics: Look for providers that offer detailed analytics and real-time performance monitoring.
- Ease of Integration: Choose a CDN that integrates well with your existing infrastructure and content management system.
- Scalability: Ensure the CDN can handle your current and future traffic needs.
- Security Features: Look for providers offering DDoS protection, Web Application Firewall (WAF), and other security features.
- Cost Structure: Compare pricing models and ensure they align with your budget and traffic patterns.
- Support: Consider the level of customer support offered, especially if you’re new to CDN implementation.
Implementing a CDN: Best Practices
- Optimize Your Origin Server: Ensure your origin server is well-optimized before implementing a CDN.
- Configure Caching Properly: Set appropriate cache expiration times for different types of content.
- Use Custom CNAMEs: Implement custom CNAMEs for a seamless user experience and easier SSL/TLS management.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly analyze CDN performance metrics and make adjustments as needed.
- Implement Content Versioning: Use versioning or fingerprinting for static assets to ensure users always receive the latest content.
- Enable Compression: Configure your CDN to serve compressed content for faster delivery.
- Utilize Preloading and Prefetching: Implement these techniques to further improve perceived load times.
Conclusion
Content Delivery Networks are an essential tool for modern websites, offering significant improvements in speed, reliability, and user experience. By leveraging the power of distributed edge servers, CDNs help businesses deliver content efficiently to a global audience while reducing costs and improving SEO performance. As the internet continues to evolve, CDNs will play an increasingly crucial role in ensuring fast, secure, and reliable content delivery across the web.
Whether you’re running a small blog or a large e-commerce site, implementing a CDN can provide substantial benefits to your online presence. Take the time to research and choose the right CDN provider for your needs, and you’ll be well on your way to delivering a superior user experience to your website visitors.